First program
This lesson will teach you how to write your first simple C++ program that can display text and perform simple calculations.
Application code
We finished the previous lesson with the following code:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello, World!";
}
Hello, World!
It displays the "Hello, World" text in the console.
Explanation
The main function
Every C++ program contains a piece of code that we call the main function. It is the first1 code that is run on the program startup.
int main()
{
}
The first line of the above code starts the function definition. It consists of a return type int, the name main, and its parameters
inside the () (none in our case). While most of these terms aren't important now, all that you should pay attention to is
the name main. Your program must always contain the main function specified in this format.
There are more variants
There are a number of ways to write the main function, but for now, we will stick to the simplest one - the one we showed above.
Sometimes you may see the main function that starts with either of the following:
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
int main(int argc, char** argv)
auto main(int argc, char** argv) -> int
auto main() -> int
While there are even more variants possible, they all do the same thing - they define the entry point of the program. We'll cover the differences between them in the future.
Blocks of code
It’s important for the program to know where main starts and ends. We use code blocks for this.
A code block in C++, is a set of instructions contained inside curly braces:
outside
int main()
{
inside
}
outside
Everything between the curly braces counts as inside the code block and everything else is outside of it.
Order of execution
The main function has a block of code that contains instructions provided by the programmer.
The computer runs the instructions in order, or in simpler words - line by line, top to bottom.
When the program is run the first line inside main is executed, then the second one and so on.
The content of the main function the first code run by the program.
In the following example, we put three instructions inside the main function to illustrate the order of execution.
You'll learn more about the std::cout later in this lesson.
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "This is an instruction that displays text.";
std::cout << "And this is another instruction that displays text.";
std::cout << "This is the third instruction that displays text.";
}
The iostream header file
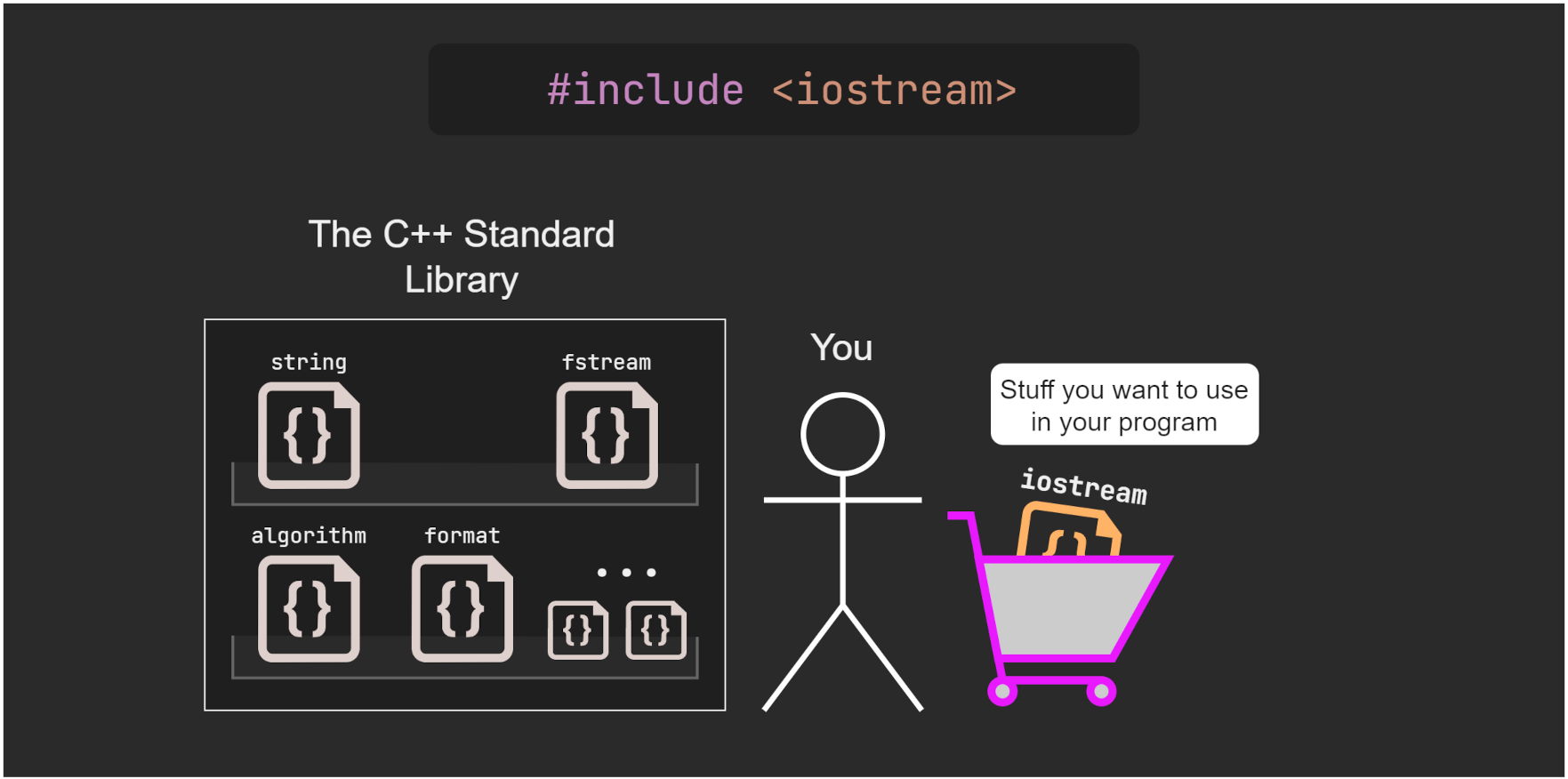
At the very beginning of the code there is a line:
#include <iostream>
This allows us to use the standard input and output tools provided by C++. The name iostream is short for input/output stream.
In practice this will let the us output text that the user can see and take input text to change what the program does.
The name iostream refers to a header file on your disk that comes with the C++ standard library.
We will explain more about them and #include in near future. For now, remember that in most cases we put
#include <header_file> at the beginning of the file.
The console
The "console" or "terminal" is the most basic form of communication for a program. It allows for a simple, two-way text interface between the program and the user. You're going to become very familiar with this tool, as you will be using it every step of the way on your journey to becoming an expert programmer.
Below are some examples of running the same code
in multiple environments. While not every terminal is the same, they will look very similar by only displaying simple text with little to no color.🖼 Overview:
As you can see many code editors like Visual Studio, VS Code, Replit.com, CLion, Vim, etc., have a console built-in into them.
Printing text to the console
To display text in the console we used the following statement inside the main block:
std::cout << "Hello, World!";
The name cout stands for a character output. It is used to send text to the console.
We will mention the std:: prefix in a minute.
For those who are curious
Strictly speaking, cout is a so-called character output stream that writes the content to a standard output, which in this case is your console,
but you don't need to remember that for the moment.
If we copy this line a couple of times
std::cout << "Hello, World!1";
std::cout << "Hello, World!2";
std::cout << "Hello, World!3";
our output changes to this:
Hello, World!1Hello, World!2Hello, World!3
A semicolon (;) separates instructions. The compiler doesn't care about instructions being written on separate lines.
The semicolon is treated as the end of the statement. For this reason, such code as below is acceptable but very illegible.
std::cout << "Hello, World!1"; std::cout << "Hello, World!2"; std::cout << "Hello, World!3";
Do not write code like this!
Presentation of the above-created program:
Note that the text was written to the console without any spaces, in a single line, and wrapped when it reached the end of the available space.
The program does exactly what it says in the code - no more, no less.
We told it that it should display the given characters... and it does.
We have to explicitly "break" the line in the right place. This will cause the following characters
to be displayed from the very beginning of the next line. To do this,
we put a special newline character inside the text: \n, like this:
std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
Note that we used the backslash (\n), and not the forward slash (/n).
This is how the program is being executed when we add newline characters:
The \n sequence represents a single character for the program.
More on that later.
Prefix of the standard namespace
std:: is the prefix of the standard library namespace from which cout comes.
Beginners often find typing std:: to be unwieldy. It can be omitted if we give the appropriate line of code beforehand:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using std::cout;
cout << "Hello, World!";
}
After the line that contains using std::cout;, the std:: prefix is no longer needed to use cout.
It lasts until the end of the current code block (the main function in this case).
In many other online tutorials and sources, it is extremely common to find usage of
using namespace std;
at the top of your file. While this is legal code in C++, it is strongly discouraged by nearly all experienced C++ programmers.
We will cover reasons for this later. For the time being, prefer the using std::cout; approach we mentioned before.
Performing calculations
Programming is used to automate certain activities. For example, we can have a computer do math for us:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "120 * 120 + 540";
}
120 * 120 + 540
Pay attention to the result of the above program!
Everything in quotation marks is treated as text, not instructions.
Therefore, instead of displaying the result of the calculation, we got what we entered in the quotation marks. To say that we want to perform some calculation, we need to remove the quotes:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << 120 * 120 + 540;
}
14940
After starting the program, we will get the correct result of the calculation in the code.
Mathematical operators
+adds two numbers together-subtracts two numbers from each other*multiplies two numbers by itself/divides two numbers by itself()parentheses order operations
C++ adheres to the "PEMDAS" order you may have learned in school.
- First Parentheses
- Then Multiplication/Division from left to right
- Finally Addition/Subtraction from left to right
Summary
You've learned about the structure of the first program's code.
For exercises visit this page.
Footnotes
-
In reality there is more code executed before the
mainfunction, that mostly deals with setting up the program but this is not important for now. ↩